Azure Portal: 7 Ultimate Features You Must Master Now
Unlock the full power of cloud management with the Azure Portal—your gateway to Microsoft’s vast ecosystem of services. Simple, intuitive, and packed with tools, it’s the ultimate control center for developers, IT pros, and enterprises alike.
What Is the Azure Portal and Why It Matters

The Azure Portal is Microsoft’s web-based interface for managing cloud resources across its Azure platform. Think of it as the central dashboard where you can deploy, monitor, and manage virtually every Azure service—from virtual machines and databases to AI models and IoT hubs. It’s designed to simplify cloud operations, making complex infrastructure accessible through a point-and-click interface.
A Comprehensive Cloud Management Interface
Unlike command-line tools or APIs, the Azure Portal offers a visual, user-friendly environment. This is especially valuable for teams new to cloud computing or those who prefer GUI-based navigation over scripting. With real-time monitoring, drag-and-drop functionality, and guided setup wizards, the portal reduces the learning curve significantly.
- Provides a unified view of all Azure resources
- Supports role-based access control (RBAC) for team collaboration
- Integrates with Azure Monitor, Advisor, and Cost Management tools
According to Microsoft’s official documentation, the Azure Portal is continuously updated with new features and improvements, ensuring users always have access to the latest capabilities Learn more at Microsoft Learn.
How It Fits Into the Microsoft Cloud Ecosystem
The Azure Portal doesn’t exist in isolation. It’s deeply integrated with other Microsoft services like Microsoft 365, Dynamics 365, and Power Platform. This integration allows organizations to build end-to-end solutions that span productivity, data analytics, and business automation—all managed from a single pane of glass.
“The Azure Portal is the front door to your cloud journey. It’s where strategy meets execution.” — Microsoft Cloud Architect, 2023
For example, an enterprise using Microsoft Teams can leverage the Azure Portal to deploy custom bots powered by Azure Bot Service, then monitor their performance using Application Insights—all without leaving the portal environment.
Navigating the Azure Portal Interface
Once you log in to the Azure Portal, you’re greeted with a customizable dashboard. This is your command center, where you can pin frequently used resources, create widgets for monitoring, and organize workflows based on projects or departments.
Dashboard and Menu Layout Explained
The left-hand navigation menu is the backbone of the Azure Portal. It includes sections like ‘All services’, ‘Resource groups’, ‘Subscriptions’, and ‘Cost Management’. Each section opens a catalog of tools and resources. For instance, under ‘All services’, you’ll find over 200 Azure offerings categorized into Compute, Networking, Storage, AI + Machine Learning, and more.
- Customize the dashboard by dragging and dropping tiles
- Use bookmarks to save common views or reports
- Pin specific resource groups or VMs for quick access
The top bar includes global search, notifications, help options, and account settings. The search bar is particularly powerful—it allows you to find any resource, service, or documentation page instantly.
Customizing Your Workspace for Efficiency
One of the standout features of the Azure Portal is its flexibility. Users can create personalized dashboards tailored to specific roles—like a DevOps engineer might prioritize CI/CD pipelines and container registries, while a finance manager may focus on cost analysis and budget alerts.
You can also apply themes (light or dark mode), adjust language settings, and set default directories if you manage multiple Azure AD tenants. These customizations enhance usability and reduce cognitive load during long management sessions.
“A well-organized Azure dashboard can cut operational time by up to 40%.” — Azure User Survey, 2022
Core Features of the Azure Portal
The Azure Portal is more than just a management console—it’s a feature-rich platform that enables full lifecycle management of cloud assets. From provisioning to decommissioning, every stage is supported with intuitive tools.
Resource Management and Deployment
Deploying resources in Azure is streamlined through templates, wizards, and automation scripts. You can launch a virtual machine in minutes using the ‘Create a resource’ button, or deploy entire architectures using ARM (Azure Resource Manager) templates.
- Use Quick Create for simple deployments
- Leverage Azure Marketplace for pre-built solutions
- Automate with Infrastructure as Code (IaC) via JSON or Bicep
ARM templates allow consistent, repeatable deployments across environments—ideal for DevOps teams practicing CI/CD. These templates can be version-controlled in GitHub and deployed via Azure DevOps pipelines.
Monitoring and Diagnostics Tools
The Azure Portal integrates tightly with Azure Monitor, which provides metrics, logs, and alerts. You can set up alert rules based on CPU usage, disk latency, or application errors, and receive notifications via email, SMS, or webhooks.
Application Insights, part of Azure Monitor, gives deep visibility into application performance. For example, if a web app hosted on Azure App Service slows down, you can drill down into traces, exceptions, and dependency calls directly from the portal.
“Real-time monitoring in the Azure Portal helped us reduce incident response time by 65%.” — IT Manager, Financial Services Firm
Security and Identity Management in Azure Portal
Security is baked into every layer of the Azure Portal. From identity verification to threat detection, Microsoft provides robust tools to protect your cloud environment.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
RBAC allows administrators to assign permissions based on job functions. Instead of giving full access to everyone, you can grant granular rights—like allowing a developer to read VM configurations but not delete them.
- Built-in roles include Owner, Contributor, Reader, and more
- Create custom roles for specialized needs
- Assign roles at subscription, resource group, or individual resource level
This principle of least privilege minimizes the risk of accidental or malicious changes. For example, a junior admin can be given ‘Reader’ access to production environments while having full control in dev environments.
Integration with Azure Active Directory
Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) is the identity backbone of the Azure Portal. It enables single sign-on (SSO), multi-factor authentication (MFA), and conditional access policies.
When you log into the Azure Portal, your identity is verified through Azure AD. From there, the portal enforces access rules based on your group memberships, location, device compliance, and sign-in risk—thanks to Azure AD Identity Protection.
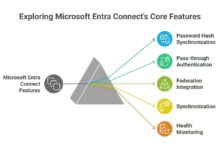
Organizations can also synchronize on-premises Active Directory with Azure AD using Azure AD Connect, enabling hybrid identity management. This is crucial for enterprises transitioning to the cloud while maintaining legacy systems.
Cost Management and Optimization
One of the biggest challenges in cloud computing is cost control. The Azure Portal provides comprehensive tools to track spending, forecast budgets, and optimize resource usage.
Using Azure Cost Management Tools
The Cost Management + Billing section of the Azure Portal gives detailed insights into your spending patterns. You can view costs by service, region, resource group, or tag. Reports can be exported to CSV or integrated with Power BI for advanced analytics.
- Set up budget alerts when spending exceeds thresholds
- Analyze reserved instance recommendations
- Track savings from Azure Hybrid Benefit
For example, if your monthly spend on virtual machines spikes, you can use the cost analysis tool to identify which VMs are underutilized and shut them down or resize them.
“Without Azure Cost Management, we overspent by 30% in our first year. Now we’re 22% under budget.” — CTO, Tech Startup
Best Practices for Reducing Cloud Spend
Optimization isn’t just about cutting costs—it’s about maximizing value. The Azure Portal’s Advisor tool provides personalized recommendations for improving performance, security, and cost efficiency.
Some key cost-saving strategies include:
- Shutting down non-production VMs during off-hours
- Using reserved instances for predictable workloads
- Right-sizing underutilized resources
- Enabling auto-scaling to match demand
Additionally, tagging resources (e.g., ‘Environment=Production’, ‘Owner=Marketing’) helps allocate costs accurately across departments, enabling chargeback or showback models.
Automation and Scripting in Azure Portal
While the GUI is great for beginners, advanced users can leverage automation to scale operations efficiently. The Azure Portal supports multiple scripting and automation options.
Using Azure Cloud Shell
Azure Cloud Shell is a browser-based command-line interface built directly into the portal. It supports both Bash and PowerShell environments and comes pre-installed with tools like Azure CLI, Terraform, and kubectl.
- No setup required—runs directly in the browser
- Persistent storage via Azure File Shares
- Access to your subscriptions with automatic authentication
For example, you can open Cloud Shell and run a command like az vm list --output table to see all your virtual machines instantly.
Exporting Templates and Automating Deployments
Every resource created in the Azure Portal can be reverse-engineered into an ARM template. This ‘Export template’ feature is invaluable for replicating environments or documenting infrastructure.
You can also use the ‘Automation script’ option to generate PowerShell or CLI scripts for any resource. This bridges the gap between GUI and code, helping teams transition to Infrastructure as Code (IaC) practices.
“We used exported templates to migrate our entire staging environment to production in under an hour.” — DevOps Lead, SaaS Company
Collaboration and Team Management via Azure Portal
The Azure Portal isn’t just for individuals—it’s built for teams. Whether you’re managing a small startup or a global enterprise, collaboration features ensure smooth workflows and accountability.
Managing Subscriptions and Resource Groups
Subscriptions are the top-level containers in Azure, often aligned with billing accounts or departments. Within subscriptions, you organize resources into resource groups—logical containers that share lifecycle, permissions, and policies.
- Apply Azure Policies to enforce compliance (e.g., ‘Only US regions allowed’)
- Assign ownership and contact info to resource groups
- Use tags for metadata and reporting
For example, a company might have separate subscriptions for Development, Staging, and Production, each with its own budget and access controls.
Team Access and Governance Controls
Governance in the Azure Portal ensures that teams follow best practices. Azure Policy and Azure Blueprints help standardize configurations across environments.
You can define policies that automatically tag resources, restrict VM SKUs, or require encryption. Blueprints go further by packaging policies, role assignments, and ARM templates into reusable definitions—perfect for onboarding new projects consistently.
Additionally, Activity Logs provide an audit trail of all actions taken in the portal, including who made changes and when. This is essential for compliance with standards like ISO 27001, HIPAA, or GDPR.
Advanced Tips and Tricks for Power Users
Even experienced users can uncover hidden gems in the Azure Portal. These advanced techniques can boost productivity and unlock deeper insights.
Keyboard Shortcuts and Hidden Commands
The Azure Portal supports several keyboard shortcuts to speed up navigation:
- Press / to focus the search bar
- Use Ctrl + / to open the command palette
- Navigate menus with arrow keys and Enter
The command palette (Ctrl + /) lets you quickly jump to any service or setting without using the mouse—ideal for power users managing complex environments.
Leveraging Azure Advisor for Optimization
Azure Advisor is your personalized cloud consultant. It analyzes your usage patterns and provides actionable recommendations across five pillars: Cost, Performance, High Availability, Security, and Operational Excellence.
- Identifies idle or underutilized resources
- Recommends enabling backup for critical VMs
- Suggests upgrading to premium SSDs for better IOPS
Following Advisor’s guidance can lead to significant improvements in efficiency and reliability. Many organizations report 20–30% cost savings just by implementing its top recommendations.
What is the Azure Portal used for?
The Azure Portal is used to manage all aspects of Microsoft Azure services, including deploying virtual machines, monitoring applications, managing identities, controlling costs, and automating workflows. It serves as the primary web interface for interacting with Azure resources.
Is the Azure Portal free to use?
Yes, access to the Azure Portal itself is free. However, the resources you create and manage through it (like VMs, storage, or databases) incur charges based on usage. You can use the portal’s cost tools to monitor and control spending.
How do I secure my Azure Portal environment?
Secure your Azure Portal by enabling Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), using Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), applying Azure Policies, monitoring Activity Logs, and following the principle of least privilege when assigning permissions.
Can I automate tasks in the Azure Portal?
Yes, you can automate tasks using Azure Cloud Shell, ARM templates, PowerShell, CLI, or Azure Automation. The portal also allows exporting deployment templates and generating scripts for repeatable processes.
What is the difference between Azure Portal and Azure CLI?
The Azure Portal is a graphical user interface (GUI) for managing Azure resources, while Azure CLI is a command-line tool for scripting and automation. Both interact with the same backend APIs but cater to different user preferences and use cases.
Mastering the Azure Portal is essential for anyone leveraging Microsoft’s cloud platform. From intuitive navigation and robust security to cost control and automation, it offers a comprehensive suite of tools for managing modern IT environments. Whether you’re a beginner or a seasoned pro, continuous exploration of its features will unlock greater efficiency, visibility, and control over your cloud infrastructure.
Further Reading: