Azure DevOps: 7 Powerful Features You Must Know in 2024
Looking to supercharge your software delivery? Azure DevOps is the ultimate platform that brings development and operations together with seamless integration, powerful automation, and enterprise-grade scalability. Let’s dive into what makes it a game-changer.
What Is Azure DevOps and Why It Matters

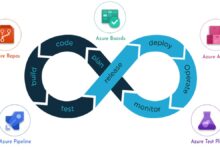
Azure DevOps is a comprehensive suite of development tools from Microsoft designed to support the entire software development lifecycle. From planning and coding to testing, deployment, and monitoring, it offers a unified platform that empowers teams to deliver high-quality software faster and more reliably. Whether you’re a startup or a global enterprise, Azure DevOps provides the infrastructure and flexibility to scale with your needs.
Core Components of Azure DevOps
Azure DevOps isn’t a single tool—it’s a collection of integrated services that work together to streamline development workflows. These include:
- Azure Repos: Git repositories or Team Foundation Version Control (TFVC) for source code management.
- Azure Pipelines: CI/CD (Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery) for automated builds and deployments across platforms.
- Azure Boards: Agile planning tools like Kanban boards, backlogs, and sprint planning.
- Azure Test Plans: Manual and exploratory testing tools to ensure software quality.
- Azure Artifacts: Package management for sharing npm, Maven, NuGet, and Python packages.
Together, these components create a cohesive ecosystem that supports modern DevOps practices. Learn more about the full suite on the official Microsoft Azure DevOps documentation.
How Azure DevOps Differs from Competitors
While tools like GitHub, Jenkins, and GitLab offer similar capabilities, Azure DevOps stands out due to its deep integration with Microsoft’s ecosystem, including Azure cloud services, Visual Studio, and Active Directory. It also supports hybrid and on-premises deployments via Azure DevOps Server, giving organizations full control over their data and infrastructure.
“Azure DevOps provides end-to-end traceability from idea to deployment, making it a strategic choice for enterprises embracing DevOps at scale.” — Microsoft Azure Case Study
Unlike GitHub Actions, which is tightly coupled with GitHub repositories, Azure Pipelines supports GitHub, Bitbucket, and even external CI systems, offering greater flexibility.
Setting Up Your First Azure DevOps Project
Getting started with Azure DevOps is straightforward. Whether you’re managing a small team or a large organization, the setup process is intuitive and well-documented. The platform supports both cloud-based (Azure DevOps Services) and on-premises (Azure DevOps Server) deployments, giving you control over where your data resides.
Creating an Organization and Project
To begin, visit dev.azure.com and sign in with your Microsoft account. You’ll be prompted to create an organization—a container for your projects. Each organization can host multiple projects, which are isolated environments for teams to manage code, work items, pipelines, and artifacts.
When creating a project, you can choose between:
- Agile – Ideal for teams using Scrum or Kanban.
- Scrum – For sprint-based development.
- CMMI – For highly regulated environments requiring detailed documentation.
Each process template defines how work items (like tasks, bugs, and user stories) are tracked and reported.
Inviting Team Members and Managing Permissions
Collaboration is at the heart of Azure DevOps. You can invite team members via email and assign roles such as Stakeholder, Reader, Contributor, or Project Administrator. Permissions are granular, allowing you to control access to repositories, pipelines, boards, and more.
Integration with Azure Active Directory (AAD) enables single sign-on (SSO) and centralized identity management, making it easier to enforce security policies across your organization.
Azure Repos: Mastering Source Control
At the foundation of any DevOps workflow is version control. Azure Repos provides both Git and TFVC options, though Git is the preferred choice for modern development due to its distributed nature and branching model.
Working with Git Repositories
When you create a new project, Azure Repos automatically initializes a Git repository. You can clone it locally using Git commands or through Visual Studio, VS Code, or other IDEs. Key features include:
- Branch policies to enforce code reviews and build validation.
- Pull requests with inline comments and threaded discussions.
- Automated merge strategies (e.g., squash, rebase, or fast-forward).
Branch policies are especially powerful—they can require approvals, status checks, and linked work items before merging, ensuring code quality and traceability.
Branching Strategies for Scalable Development
Effective branching is critical for team collaboration. Azure DevOps supports several strategies:
- Main-Only (Trunk-Based): All developers commit to a single main branch with short-lived feature branches.
- GitFlow: Uses develop, feature, release, and hotfix branches for structured releases.
- GitHub Flow: Simpler than GitFlow, focusing on feature branches and continuous deployment.
For enterprise teams, combining trunk-based development with feature toggles allows continuous integration without disrupting production.
Azure Pipelines: Automating CI/CD Like a Pro
One of the most powerful aspects of azure devops is its CI/CD engine—Azure Pipelines. It enables automated builds, tests, and deployments across multiple platforms, including Windows, Linux, macOS, and even Kubernetes clusters.
Building Your First Pipeline
You can create pipelines using YAML or the classic visual editor. YAML is recommended because it allows you to version-control your pipeline configuration alongside your code.
Here’s a simple example of a YAML pipeline:
trigger:
- main
pool:
vmImage: 'ubuntu-latest'
steps:
- script: echo Hello, Azure DevOps!
displayName: 'Run a one-line script'
- script: |
echo Adding useful tools
sudo apt-get update
displayName: 'Run a multi-line script'This pipeline triggers on every push to the main branch, runs on the latest Ubuntu image, and executes two shell scripts. You can expand this to include testing, packaging, and deployment steps.
Multi-Stage Pipelines for Complex Workflows
Modern applications often require deployment across multiple environments—dev, staging, and production. Azure Pipelines supports multi-stage workflows where each stage represents a deployment environment.
- Stages can have manual approvals, gates, and pre-deployment conditions.
- You can deploy to Azure App Service, VMs, Kubernetes, or even AWS and GCP.
- Integration with Azure Monitor and Application Insights enables deployment tracking and health checks.
For example, a production stage might require two approvers and a successful smoke test before deployment proceeds.
Azure Boards: Agile Project Management Simplified
Delivering software isn’t just about code—it’s about collaboration, planning, and visibility. Azure Boards brings agile practices into the development workflow with tools that help teams plan, track, and discuss work across the lifecycle.
Using Kanban Boards and Backlogs
Kanban boards in azure devops provide a visual way to manage work. You can create custom columns (e.g., To Do, In Progress, Review, Done), set work-in-progress (WIP) limits, and drag-and-drop tasks to reflect progress.
Backlogs allow you to prioritize user stories and tasks. You can organize them into epics, features, and user stories, creating a hierarchical structure that aligns with business goals.
Sprint Planning and Velocity Tracking
For Scrum teams, Azure Boards supports sprint planning with capacity management and task assignment. You can define sprint durations, assign team capacity (in hours or story points), and allocate work items accordingly.
Velocty charts help teams measure how much work they complete per sprint, enabling better forecasting and planning. Burn-down charts visualize progress, helping identify bottlenecks early.
Azure Test Plans: Ensuring Quality at Speed
Testing is a critical component of DevOps. Azure Test Plans provides tools for manual, exploratory, and automated testing, ensuring that quality is built into every release.
Manual Testing and Test Suites
You can create test plans, test suites, and test cases directly in Azure DevOps. Test suites can be requirement-based (linked to user stories) or static (predefined sets of tests).
During manual testing, testers can log results, attach screenshots, and report bugs—all within the same interface. This tight integration ensures traceability from requirement to test to bug.
Exploratory Testing and Feedback
Exploratory testing allows QA engineers to test without predefined scripts, simulating real-world user behavior. Azure Test Plans captures session data, including steps taken, notes, and screen recordings.
The Feedback client enables stakeholders to provide real-time feedback on web or mobile apps, routing suggestions directly into Azure Boards as work items.
Azure Artifacts: Managing Packages Across Teams
Modern applications depend on reusable components—libraries, frameworks, and utilities. Azure Artifacts helps teams share and manage these packages securely across projects and organizations.
Creating and Publishing NuGet Packages
You can create a feed in Azure Artifacts to host NuGet, npm, Maven, or Python packages. Once created, developers can publish packages using CLI tools or CI pipelines.
For example, to publish a NuGet package:
nuget push *.nupkg -Source "https://pkgs.dev.azure.com/yourorg/_packaging/yourfeed/nuget/v3/index.json" -ApiKey azThis integrates seamlessly with Azure Pipelines, allowing automated package versioning and publishing on every successful build.
Consuming Packages in Your Projects
Teams can consume packages by adding the feed as a package source in their development environment. For .NET projects, this means updating the NuGet.Config file. For Node.js, it involves configuring .npmrc.
Private feeds ensure that sensitive internal packages are not exposed to public registries, enhancing security and compliance.
Integrating Azure DevOps with External Tools
No tool works in isolation. Azure DevOps offers extensive integration capabilities with third-party services, enhancing its functionality and flexibility.
Connecting with GitHub and Slack
You can connect Azure Pipelines directly to GitHub repositories, enabling CI/CD for code hosted outside Azure Repos. This is ideal for open-source projects or teams already invested in GitHub.
Slack integration allows teams to receive notifications about build status, pull requests, and work item updates directly in their Slack channels, improving visibility and response time.
Using Extensions from the Marketplace
The Azure DevOps Marketplace offers hundreds of extensions—from SonarQube and Checkmarx for code quality to Jira and Trello for project management. These can be installed with a few clicks, extending the platform’s capabilities without custom development.
Best Practices for Scaling Azure DevOps in Enterprise
As organizations grow, so do their DevOps needs. Scaling azure devops requires thoughtful planning around governance, security, and automation.
Implementing Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
Use groups and permission sets to manage access at scale. For example, create a “DevOps Admins” group with full pipeline management rights, while developers have contributor access.
Avoid using personal access tokens (PATs) for long-term automation—instead, use service connections and managed identities for secure, auditable access.
Enforcing Pipeline as Code and Governance
Treat pipeline configurations as code. Store YAML files in repositories, review them via pull requests, and apply branch policies to prevent unauthorized changes.
Use pipeline templates to standardize common workflows across teams, reducing duplication and ensuring compliance with organizational standards.
Monitoring and Auditing with Logs and Analytics
Enable audit logs to track user actions, pipeline runs, and configuration changes. Integrate with Azure Monitor and Log Analytics to gain insights into usage patterns, performance bottlenecks, and security events.
Set up alerts for failed builds, unauthorized access attempts, or unexpected deployment activities.
What is Azure DevOps?
Azure DevOps is a Microsoft platform that provides a suite of tools for planning, developing, testing, and deploying software. It includes services like Azure Repos, Pipelines, Boards, Test Plans, and Artifacts to support end-to-end DevOps practices.
Is Azure DevOps free to use?
Yes, Azure Devops offers a free tier for small teams with limited users and pipeline minutes. Paid plans are available for larger teams and enterprises needing more resources and advanced features.
How does Azure Pipelines differ from Jenkins?
Azure Pipelines is cloud-native, integrates seamlessly with Azure services, and supports YAML-based configuration with built-in scalability. Jenkins is open-source and self-hosted, requiring more maintenance but offering extensive plugin support.
Can I use Azure DevOps with GitHub?
Absolutely. Azure Pipelines can connect to GitHub repositories, allowing you to trigger builds and deployments directly from GitHub commits and pull requests.
What is the difference between Azure DevOps Services and Server?
Azure DevOps Services is the cloud-hosted version, while Azure DevOps Server is the on-premises version. Both offer similar features, but the Server version gives organizations full control over infrastructure and data.
Azure DevOps is more than just a toolset—it’s a complete ecosystem designed to accelerate software delivery while maintaining quality and security. From agile planning with Azure Boards to automated CI/CD with Azure Pipelines, every component is built to support modern development practices. Whether you’re a solo developer or part of a global enterprise, mastering azure devops can transform how you build and deliver software. By leveraging its powerful features, integrations, and best practices, you can achieve faster time-to-market, improved collaboration, and greater operational efficiency. The future of software development is integrated, automated, and intelligent—and Azure DevOps is leading the way.
Further Reading: